Many of us do not realize what effect it has on the functioning of the human organism, but also on everything living on our Earth, the alternation of intensities and colors of light and darkness. More clarity on this issue lies with those who have accepted the Women's Network's invitation to a great lecture on Thursday, January 25, 2024. The topic Our everyday light and its influence on eyesight and on our circadian rhythm (biorhythm) was accompanied by Dr. Zuzana Prepiaková, PhD from the Clinic of Pediatric Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine UK and NÚDCH in Bratislava. She is a member of the Slovak Society of Ophthalmology, the Slovak Medical Chamber and the World Society of Paediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (WSPOS) and has a rich lecturing and publishing activities.
The natural light that the human eye is able to perceive has all the colors of the rainbow. Purple, blue, green, orange and red. Outside, the spectral composition of light changes. At noon it is very intense, it contains many wavelengths of blue and green. We need them especially during the day. Blue light charges us, gives us energy, a feeling of joy, satisfaction. Towards the evening of blue and green decreases, orange and red set in, then night comes. And our organism has been accustomed to this alternation of light intensity and color for thousands of years. And our body is adapted to this, which is subject to circadian rhythm – a regular rhythmic alternation of physical and mental changes in the 24-hour cycle of day and night. To put it simply, during the day active processes take place at the level of cells and organs, at night regenerative. Whether it is day or night, information comes to the brain through the eyes. Accordingly, hormones are triggered and other organs work. During the day, the most important thing is natural blue light, its intensity and strength. Exclusively at night, the hormone melatonin, the hormone of darkness, which has been found in all organisms studied so far, is produced. It helps a lot in the organization of biorhythm and is responsible for the regenerative processes in our body. It belongs to the strongest antioxidants, protects us from cancer, strengthens the immune system. It is very important in maintaining a good mood and also for memory and learning or reproduction. Light, especially blue, prevents its formation.
In the past, people spent most of their time outdoors, during the day they had enough natural light, regulating our biorhythms, alertness, good mood, cognitive abilities, performance. After dark, they lit only fires, later lamps.
However, everything changed in 1879 with the discovery of the incandescent lamp...
What does it look like today? During the day we have little natural light, in the evening and at night an excess of artificial light, which significantly disrupts the biorhythm before and after sunset, brings the possibility of various health risks, so-called digital fatigue and cancels the supply of melatonin.
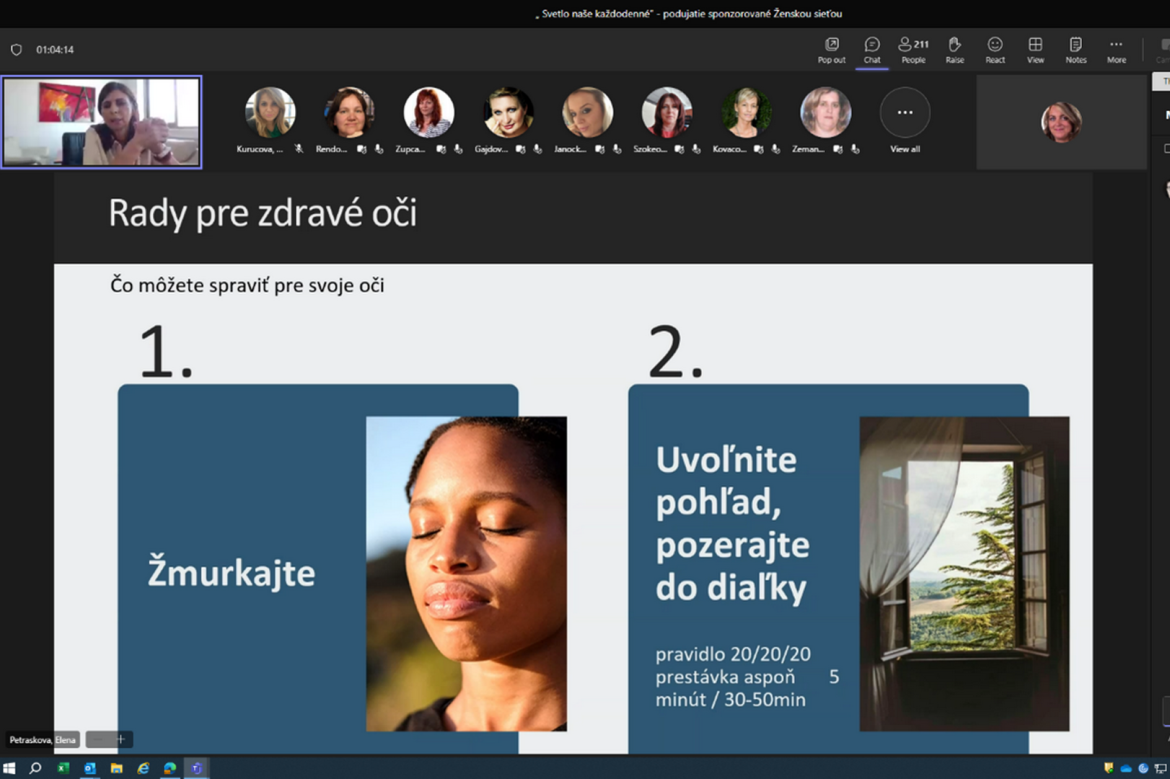
What can we do for our health?
Zuzana Prepiaková recommends exposing yourself to direct natural light as much as possible during the day. You need to put the workbench as close to the window as possible, not to cover the blinds, but, on the contrary, to pull them out. Short, so-called sunny breaks, walks outdoors will also help a lot. Ventilation is also important. At home, in the office, but also in the car, for example. Not only because of the fresh air, but also because with the window open, part of the UVA radiation gets inside. We should use sunglasses judiciously. When we put them on, our body "thinks" that it is getting dark, that night is approaching and begins to produce melatonin. Sunglasses shouldn't be the first thing we put on as soon as we leave the house. They should be used sparingly.
In the evening, the doctor advises reducing the light intensity. When the sun is after sunset, we should not immediately turn on a large intense light from above. We prefer more concentrated light, while it is good to use sources without the blue and green components of light and also make sure that it does not illuminate our eyes so much. "If possible, it's a good idea to reduce blue light from electronic devices an hour and a half before bedtime. The ideal sleep is in complete darkness. There are black out curtains that do not let light through. If we don't have them, we can put a scratch on our eyes. Of course, let's keep safety in mind," suggests ophthalmologist Zuzana Prepiaková.
Blue light in the evening can be reduced. There are various tips and tricks for this.
For example, on the mobile we set the so-called night mode or red filter, in the case of androids you can download the Twilight application. On computers, when you work even in the evening, F.Lux or Iris mini applications are suitable. More modern TVs offer blue light reduction options. It should also be noted that different wifi devices, microwave ovens, radios and the like, have different lights that often glow green or blue. They can be pasted over with a special film. Wise people also invented a vitae bulb that supports the natural circadian rhythm and that can also be adjusted to red light. The simplest solution is blue light blocking glasses.
And a few more tips for healthy eyes.
When we are very focused while working at the computer or reading, we do not even realize that we forget to blink. Outdoors in nature, we blink once, twice every ten seconds. So you have to blink, it relaxes our eye muscles. And also to look into the distance or transmit the view from afar to close.
"I wish you lots of light during the day and darkness at night. Let's realize that light is a biologically active substance, and when we start treating it with respect, it could be the key to restoring our health. Even small changes will make a lot," said Zuzana Prepiaková to the participants of an undoubtedly interesting lecture, during which she also answered curious questions.












